Let’s cut the pretense: If you’re reading this right now, you’re interested in financially improving yourself in the new year.
But at the risk of sending you packing by the second paragraph, truth be told, I don’t much believe in New Year’s resolutions.
More often than not, making a New Year’s resolution is a way to get yourself to do something you think you should be doing. That in and of itself is admirable! We’re humans! We’re certainly not perfect! And we absolutely should improve ourselves! So if you think you need a New Year’s resolution, your brain is in the right place!
The problem? New Year’s resolutions are often too grand and focus too heavily on the end goals. “I’m going to lose 50 pounds by 2026” sounds fantastic! But big goals take time. And many people get frustrated and quit when, a few weeks or months later, they haven’t met their objective … even if it was always going to take a year to reach!
So our job today isn’t to start your marathon to financial soundness—some glorious finish line for you to cross come Dec. 31, 2025.
Our job today is getting you to your first small money victories. And no matter when you start—Jan. 1 or April 27 or Sept. 15—these little wins will serve the healthy foundation from which you can reach for bigger and better financial aspirations down the road.
Featured Financial Products
Financial New Year’s Resolutions

Anecdotally, we probably all know at least one person who has said that [pick a year!] is the year they’re going to get their financial house in order.
Well, financial New Year’s resolutions don’t just feel ubiquitous—the stats back it up.
Allianz Life recently released the results of its annual New Year’s Resolution Study, and it found that 38% of American adults are making financial stability their No. 1 focus area in the coming year. That marks the highest percentage recorded over the past decade.
Young and the Invested Tip: Is your resolution to get on top of your retirement plan? You can start right away by subscribing to our new FREE newsletter, Retire With Riley.
Little wonder there.
Americans are plenty stressed with their financial situations as we head into 2025. Of those surveyed, 44% say their stress about finances is about the same as it was in the prior year, and another 41% say they’re even more stressed. And contributors to that stress are no less surprising:
— Cost of day-to-day expenses (54%)
— Income or retirement income is too low (49%)
— Haven’t saved enough for an emergency fund (35%)
— Too much debt (35%)
“Americans who are looking to improve their financial health in 2025 can work with a financial professional who can help them create a strong financial strategy for their future,” says Kelly LaVigne, vice president of Consumer Insights, Allianz Life. “That strategy can help decrease stress by providing a guide for how to curb excessive spending and prioritizing saving.”
Practical Financial New Year’s Resolutions for 2025

In our view, that strategy should start with simple, humble steps. Much like Rome, discipline isn’t built in a day. And if you kick off 2025 with some grand proclamation about how you’re going to have $50,000 in your savings account a year from now … well, you’ll probably be off the path by February.
So, here are five simple financial New Year’s resolutions, complete with easy, actionable steps:
1. I’m going to make a budget.
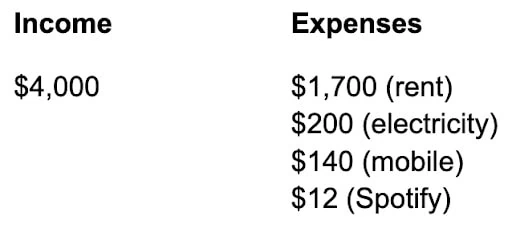
Get a pen and paper. Or if you prefer, open up Notebook, Notes, Word, whatever it is you use to write things down on your computer, tablet, or phone.
On the left, write down your monthly take-home income. On the right, jot down three or four recurring monthly bills. Don’t go looking for anything—just write down the bills you can remember off the top of your head. An example of such a template is in the image above.
Congratulations! In what was likely literally less than two minutes, you have already started a budget.
To finish your simple budget, you really only need to do two more things:
— Look through your bills and bank/credit accounts and write down the rest of your monthly expenses.
— Separate your “need” expenses (rent, electricity, food) from your “want” expenses (streaming services, restaurant spending, etc.)
That’s it! That’s a simple budget that gives you a picture of how much money you have coming in every month, as well as where that money goes every month. It is one of the most basic stepping stones for most of the financial decisions you’ll ever make.
You can do plenty more with your budget—budgeting apps, for instance, have more attractive interfaces and can provide additional tools to help you make the most of your budget.
But it’s plenty easy to upgrade to a more sophisticated budget all by yourself. We even have a free budget template you can use to level up.
Featured Financial Products
2. I’m going to spend less.

A budget will show you whether you’re spending too much on “wants.” But some people don’t even need a budget to know they need to cut back their non-essential purchases. They just know.
Young and the Invested Tip: Financial minimalism isn’t just a way to spend smarter—it can even help you reduce stress.
Either way, don’t mindlessly cut all of your non-essential spending unless you must to make ends meet. If you’re simply trying to free up more money for, say, savings, cutting out everything will just lead to relapse. Instead, be thoughtful and tactical about where you cut “fun” spending.
A super-simple way to start is the 90/90 rule. This is actually a decluttering method, but you can use it to determine which of your discretionary expenses should be the easiest to get rid of!
Look at each of your non-essential purchases over the past month. For each one, ask yourself two questions:
1. Have I used this item in the last 90 days?
2. Will I use it in the next 90 days?
You have to be a little interpretive, but it can be helpful. For instance:
If you bought Dunkin a few times in the past 90 days, and you think you would go again a few times in the next 90 days, then hey, Dunkin might be more important than other discretionary purchases.
If you paid for a month of a streaming service you haven’t watched in 90 days, and you don’t really have any concrete plans to watch it in the next 90 days … you can probably stop subscribing to that streaming service. After all: You can always resubscribe if that service adds shows you really plan to watch.
3. I’m going to pay myself.

“Paying yourself first” refers to the idea of putting your savings ahead of your discretionary purchases in your budget. It sounds commonsensical, but many people don’t do this. Visually, many people treat savings like this:
1. Set aside money for essential purchases (rent, utilities, etc.).
2. Make discretionary purchases (restaurants, movie tickets, etc.).
3. Save whatever’s left over.
When you pay yourself, you’re treating your savings like this:
1. Set aside money for essential purchases
2. Set aside money for savings.
3. Make discretionary purchases with whatever’s left over.
Here are two easy ways to get started:
401(k): If you have access to a 401(k) but don’t contribute to it, start contributing to it. Setting up automatic contributions should take less than three minutes. If you don’t know how, ask your HR or benefits provider for help. Money will be taken out of your paycheck—pretax, which benefits you!—automatically every pay period. You’ll never have to think about it ever again. And if you already contribute, step up your game too—max out your 401(k)!
Bank: Set your checking account to make an automatic transfer to your savings account every time you get paid. How you go about this will depend on your pay schedule (monthly, bimonthly, every two weeks, etc.) and your particular bank platform. Ask a local bank representative or call site support for directions that are specific to your bank. (Automatic savings apps are another way to go about this.)
4. I’m going to invest.

While there is a wide world of investments to explore, most people begin in the stock market. And investing in stocks has never been easier, been quicker, nor required less money than it does today.
Young and the Invested Tip: Want to really dive into your investing education? Check out all of our investing topics here.
If you want to get started, follow these simple steps:
Step 1: Check out our list of brokerage accounts that support fractional shares.
Fractional share brokerages allow you to buy “pieces” of stocks and even exchange-traded funds for just $10, $5, or as little as $1 at a time. In other words: Even if you can only set aside $10 or $20 a month, you can start building a truly diversified portfolio.
Step 2: Open an account.
We’ve personally reviewed dozens of accounts, and this often involves opening trial accounts from scratch. We can confidently say this rarely takes more than 10 minutes and requires basic information you either have memorized or have laying around.
Step 3: Fund the account.
Most fractional brokerage accounts require no initial deposit, but a few do. Either way, you’ll want to fund the account with at least a little money to get started. And per the idea of “paying yourself,” we recommend setting an auto-transfer from your bank every month. (Some brokers even give free shares of stock for opening and funding an account.)
Step 4: Select/buy your investments.
One thing we can’t help you do overnight is learn how to invest. That takes time. But if you want to put your money to work quickly, two of the best places to start are index funds or target-date funds. (Note: Most target-date funds are mutual funds, but if you can only work with exchange-traded funds [ETFs], iShares offers a suite of target-date ETFs.)
Featured Financial Products
5. I’m going to stop keeping up with the Joneses.

OK, to be fair, this isn’t a common resolution, but it darn well should be.
One of the most insidious sources of financial problems comes from a combination of envy and pride. It’s often referred to as “keeping up with the Joneses”—a desire to want to keep up with your neighbors in a material sense. This drives you to acquire more stuff, in the hopes you can show the world you’re just as good as them.
It’s an irresponsible way of thinking to begin with. But “neighbors” have become “everyone else with an internet connection,” and that’s just too high a bar for virtually anyone to clear. Somewhere, someone will always have more than you.
And frankly, social media frequently provides an incomplete picture—you see breathtaking vacations or a Pinterest-perfect home, but you don’t see crippling debt or deep-seated depression.
Beating back the desire to keep up with the Joneses doesn’t have a quick fix. There’s no app for that. It’s a mindset you have to work on over time.
But if you can teach yourself to stop caring about what other people think, and only focus on the happiness of you and your family, you’ll find that mindset runs awfully parallel to savvy financial decision-making.
Related: 12 Best Long-Term Stocks to Buy and Hold Forever
As even novice investors probably know, funds—whether they’re mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs)—are the simplest and easiest ways to invest in the stock market. But the best long-term stocks also offer many investors a way to stay “invested” intellectually—by following companies they believe in. They also provide investors with the potential for outperformance.
So if you’re looking for a starting point for your own portfolio, look no further. Check out our list of the best long-term stocks for buy-and-hold investors.
Related: 9 Best Monthly Dividend Stocks for Frequent, Regular Income

The vast majority of American dividend stocks pay regular, reliable payouts—and they do so at a more frequent clip (quarterly) than dividend stocks in most other countries (typically every six months or year).
Still, if you’ve ever thought to yourself, “it’d sure be nice to collect these dividends more often,” you don’t have to look far. While they’re not terribly common, American exchanges boast dozens of monthly dividend stocks.
Please Don’t Forget to Like, Follow and Comment
Did you find this article helpful? We’d love to hear your thoughts! Leave a comment with the box on the left-hand side of the screen and share your thoughts.
Also, do you want to stay up-to-date on our latest content?
1. Follow us by clicking the [+ Follow] button above,
2. Subscribe to Retire With Riley, our free weekly retirement planning newsletter, and
3. Give the article a Thumbs Up on the top-left side of the screen.
4. And lastly, if you think this information would benefit your friends and family, don’t hesitate to share it with them!




